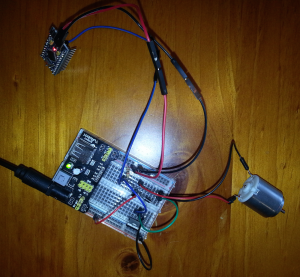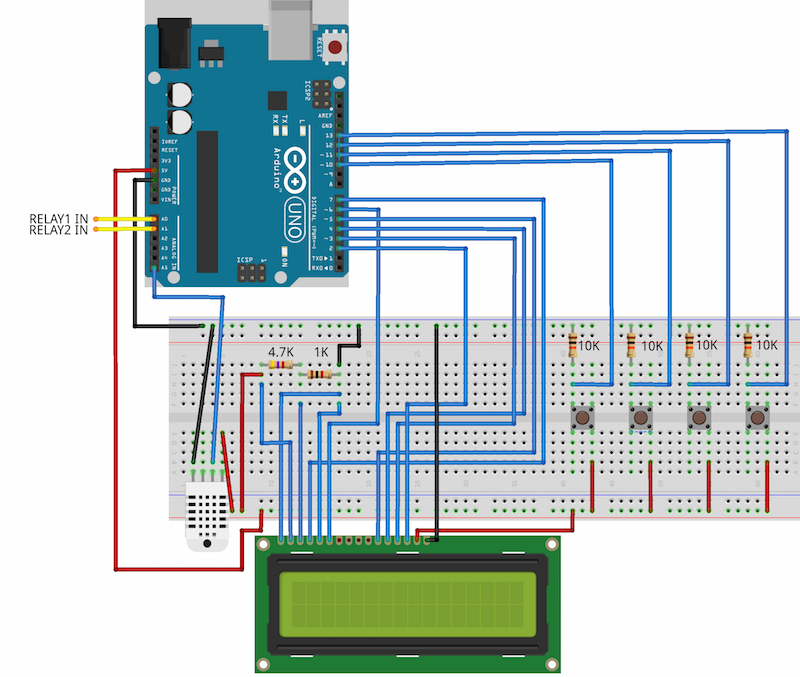
This project is about driving a two speed fan with an Arduino, based on the environment’s temperature.
The project has been designed to help automating an existing fire-based heating system. The idea is that the environment will be warmed faster, by driving heated air into the room with a multi speed fan, while the fire is hot and the surrounding environment not yet.
I wanted to make it a little more interesting by adding a LCD display to show temperature, humidity and fan status, and four buttons to increase and decrease the two temperature values that drive the fan speeds.
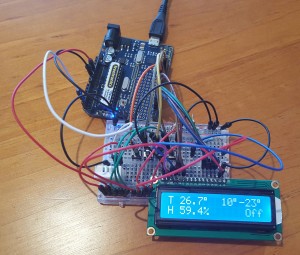
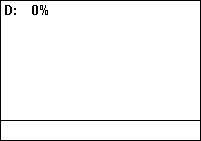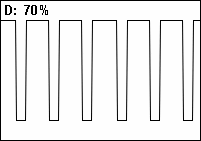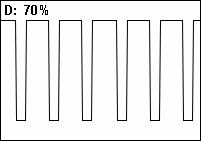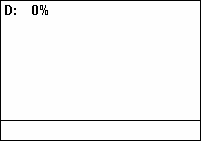
When the temperature is below the lowest temperature threshold, the fan will be running at full speed. With temperatures between the lowest and the highest threshold the fan will be running at half speed and with temperatures above the highest threshold the fan will be off.
This project demonstrates the use of an Arduino (or compatible) micro controller with a temperature and humidity sensor to drive outputs, it demonstrates the usage of a LCD display, push buttons and EEPROM memory storage.